By Description: 177
An electronic ballast is an electronic device that uses electronic technology to drive an electric light source to produce the required lighting. More and more modern fluorescent lamps use electronic ballasts, which are light and compact, and can even integrate electronic ballasts with lamp tubes.ballasts lowes
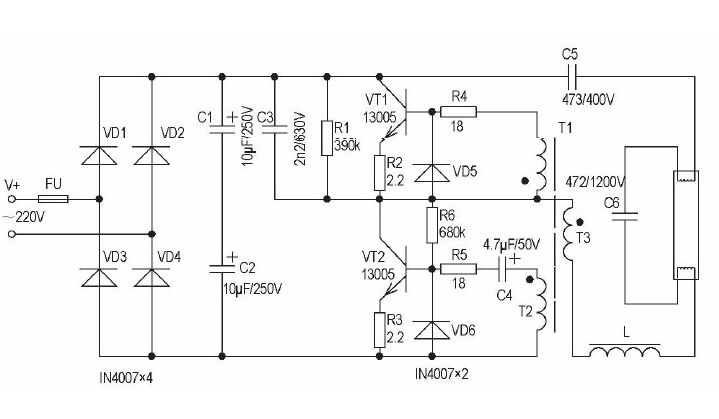
Due to the use of modern soft-switching inverter technology, advanced active power factor correction technology and electronic filtering measures, the electronic ballast has good electromagnetic compatibility and reduces the loss of the ballast itself.
Electronic ballast is an electronic control device that uses semiconductor electronic components to convert DC or low-frequency AC voltage into high-frequency AC voltage to drive low-voltage gas discharge lamps, tungsten-halogen lamps and other light sources. The most widely used is the electronic ballast for fluorescent lamps.ballasts electrical
Ⅰ. Advantages of electronic ballasts:
1. Fast start-up: Electronic ballasts can achieve fast start-up and re-lighting, reducing waiting time and flickering.
2. Dimming performance: Electronic ballasts usually have a dimming function, which can adjust the brightness of lighting equipment by controlling the working mode of electronic components.ballasts for lights
3. Less electromagnetic interference: Compared with magnetic ballasts, electronic ballasts generate less electromagnetic interference and less interference to surrounding electronic equipment.
4. High energy efficiency: Compared with magnetic ballasts, electronic ballasts have higher energy efficiency and can provide higher light efficiency and lower energy loss.
5. Small size and light weight: Electronic ballasts usually use integrated circuits and electronic components to make them smaller and lighter, suitable for compact lamp designs.
6. High-frequency operation: Electronic ballasts use high-frequency technology to drive lighting equipment, avoiding the visible flicker problem that exists in traditional ballasts.
Ⅱ. Classification of electronic ballasts
1. High efficiency electronic ballast:
The general electronic type is collectively referred to as high efficiency, because the electronic type is high frequency, and the power factor is better than the traditional type. Used to regulate current and voltage to provide a stable power supply to devices that require specific current and voltage. Compared with traditional magnetic ballasts, high-efficiency electronic ballasts use advanced electronic components and design techniques to improve energy conversion efficiency and reduce energy loss.
2. Instant start electronic ballast without preheating:
Instant start non-preheating type electronic ballast, the lamp tube instantaneous start does not need warm-up time when lighting, but because the filament at the end of the lamp tube bears the sudden large starting voltage, the filament of the lamp tube is easy to break after a short time, and the life of the lamp tube shorter. Traditional electronic ballasts usually require a warm-up period to ensure that the lamp can start properly and reach the rated brightness. This is because during the preheating process, the ballast will provide a high starting voltage and current to light the gas discharge tube.
3. Preheating type starting electronic ballast:
The preheating type starting electronic ballast is an electronic ballast, which is used for preheating operation before lighting the gas discharge lamps (such as fluorescent tubes). By controlling the starting current and voltage, the lamps can be started safely and stably. at rated brightness. Preheating type starting electronic ballast, the circuit is designed to start slowly, and the lamp will not light up until about 1-2 seconds when the light is turned on. The filament at the end of the lamp only bears the starting voltage that is slowly boosted, and the filament of the lamp is not easy to break , The lamp is more durable. Traditional gas discharge lamps need a certain amount of time to preheat the gas discharge tube to make it reach a suitable working state. The preheating type starting electronic ballast starts and preheats the gas discharge tube by providing proper current and voltage, so that it can generate a stable discharge.
Ⅲ. Advantages and disadvantages of electronic ballasts
1. Advantages:
Dimming performance: Most electronic ballasts have a dimming function, which can adjust the brightness of lighting equipment by controlling the operation of electronic components.
High power factor: Electronic ballasts can achieve high power factor and reduce the negative impact on the power system.
High-frequency operation: Electronic ballasts use high-frequency technology to drive lighting equipment, avoiding the visible flicker problem that exists in traditional ballasts.
High energy efficiency: Compared with magnetic ballasts, electronic ballasts have higher energy efficiency and can provide higher light efficiency and lower energy loss.
Small size and light weight: Electronic ballasts use integrated circuits and electronic components, so they are smaller and lighter, suitable for compact lamp designs.
2. Disadvantages:
Sensitivity to environmental conditions: Electronic ballasts are sensitive to environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity, so it is necessary to pay attention to environmental adaptability and heat dissipation issues during installation and use.
Higher cost: Compared with traditional magnetic ballasts, the initial cost of electronic ballasts is usually higher.
Sensitivity to electromagnetic interference: Electronic ballasts need to pay special attention to suppressing electromagnetic interference during design and manufacture to avoid interference with surrounding equipment. This may require additional EMC measures.
Ⅳ. Working principle of electronic ballast
1. Current regulation: Electronic ballasts use electronic components (such as transistors, power switches, etc.) and circuit design to regulate current.
2. Protection function: Electronic ballasts usually have a variety of protection functions to ensure the safe operation of electronic equipment and circuits. These functions can include overload protection, over temperature protection, short circuit protection, etc. to prevent damage and failure.
3. Output circuit: The output circuit supplies the regulated current to lamps or other electronic devices. The output circuit is usually composed of inductors, capacitors, semiconductor components, etc. to provide stable current and filter.
4. Control circuit: The control circuit of the electronic ballast is responsible for monitoring and controlling the stability of the output current. It usually consists of a control chip, sensors and feedback circuits. The control circuit can adjust the output current of the electronic ballast as needed to maintain stable brightness and current supply.
5. Input circuit: Electronic ballasts are usually connected to the AC power supply, and the input voltage is rectified and filtered through the input circuit. The input circuit usually includes components such as rectifier diodes and filter capacitors to convert AC power into DC power.
Ⅴ. Application fields of electronic ballasts
1. Medical equipment: Electronic ballasts are also used in medical equipment, such as operating room lighting, medical imaging equipment, phototherapy equipment, etc.
2. Home lighting: Electronic ballasts are widely used in home lighting, such as LED lamps, fluorescent lamps, energy-saving lamps, etc. They provide efficient current control and stable lighting effects.
3. Industrial lighting: In the environment of factories, warehouses and production facilities, electronic ballasts can be used to drive high-intensity gas discharge lamps (such as metal halide lamps, high-pressure mercury lamps, etc.) and other industrial lighting equipment.
4. Street lighting: Electronic ballasts are used in urban street lighting systems, such as street lights and landscape lighting. They provide reliable current control and long lamp life operation.
5. Automotive lighting: Electronic ballasts are used in automotive lighting systems, such as headlights, taillights, and instrument panel lighting. They can provide a stable current supply and increase the brightness and life of the lamp.
Ⅵ. Technical terms of electronic ballasts
1.THD Total Harmonic Distortion
When the ballast and the lamp work at the rated power supply voltage, after the lamp reaches a stable working state, the sum of the odd harmonic components in the input power supply current. According to Beaulier's definition, the rectangular wave is formed by the superposition of a series of sine waves with a common period but different frequencies. The greater the harmonic content, the greater the damage to the input sine wave.
2. CF crest factor
Under the rated power supply voltage, when the ballast and the lamp work together, when the lamp reaches a stable working state. The ratio of the peak value of the current state output current flowing through the lamp to the root mean square value CF=PK/rms.
3.EMC
The equipment or system can work normally in the electromagnetic environment and does not cause unacceptable electromagnetic disturbance to anything in the environment. There are different implementation standards in Europe and America.
4.PF power factor
The combination of ballast and lamp effectively utilizes the input power of the power supply, which is also expressed as Watt/VA or COSΦ in some places. Generally speaking, the PF of magnetic ballasts is 0.5, and even after capacitance correction, it can only reach about 0.8, while electronic ballasts can usually achieve 0.95~0.99. Watts of electricity.
Ⅶ. Precautions for electronic ballasts
The electronic ballast directly rectifies the mains power, and then performs half-bridge inverter to light the fluorescent tube. It is not isolated from the mains, just like the hot bottom plate of a TV, the circuit board is charged everywhere, and the human body is in danger of electric shock if it touches the public line (ground line), so special attention should be paid to personal safety during maintenance. When installing electronic ballasts, be sure to follow the manufacturer's installation guidelines. Correct installation and wiring can ensure the normal operation and safety performance of electronic ballasts.
After power on, do not touch any metal part of the circuit board with your hands, especially do not hold the circuit board with both hands. Electronic ballasts generate heat during operation, so proper cooling conditions need to be maintained. Ensure adequate space and ventilation around the electronic ballast to avoid performance degradation or damage due to overheating. When installing, maintaining or replacing electronic ballasts, be sure to disconnect the power supply first. Avoid the risk of electric shock and short circuits.

Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between electronic ballasts and traditional magnetic ballasts?
There are some differences between electronic ballasts and traditional magnetic ballasts in terms of working principle, performance and characteristics. Electronic ballasts use electronic components and circuits to control and regulate current supply, and drive lamps through high-frequency switching circuits. The inductive ballast limits the current through the electromagnetic induction generated by the inductance coil, and adjusts the current through the magnetic regulator. Electronic ballasts are relatively small and lightweight, and due to the high frequency switching circuit, smaller components and coils can be used, reducing size and weight. Magnetic ballasts, on the other hand, are usually larger and heavier due to the use of larger-sized components such as inductor coils.
Electronic ballasts generally have a longer life and better reliability. Due to the high-frequency switching circuit, the operating temperature of the electronic ballast is lower, which reduces the heat accumulation of the components, thereby prolonging the life. However, components such as coils and magnetic regulators in magnetic ballasts are easily affected by heat, and their lifespan is relatively short.
2. What is the basis for purchasing electronic ballasts?
Load type: Determine the type of electronic ballast required, and select the appropriate electronic ballast according to the type of lamp to be driven.
Environmental adaptability: According to the actual application environment, select an electronic ballast with appropriate protection level, temperature resistance and waterproof performance to ensure that it can adapt to the working environment.
Power requirements: Select the appropriate electronic ballast according to the power of the lamp to be driven. Make sure that the rated power range of the electronic ballast can meet the needs of the lamp.
Quality and reliability: Choose well-known brands or electronic ballast products with good reputation to ensure their quality and reliability. See user reviews, product specifications, certification information, and more.